Introduction to CSS for web development
Beginner CSS // Basics of CSS // Learn CSS // CSS fundamentals for web development
Hello and welcome!! 🤩🤩
Today, we will get into what it is really about 🤣🤣 THE ALMIGHTY CSS
CSS is...

CSS is about to become the bane of your existence as a web developer.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is the code that styles web content. Like HTML, CSS is not a programming language. It's not a markup language either. CSS is a style sheet language. CSS is what you use to selectively style HTML elements.
CSS, when added to HTML, is what gives all the color and style to a website. If you recall from our first HTML lesson, we had an example of what a website looks like with just pure HTML, that is, without any styling.
Let us get right into it!!! 🥳🥳🥳
NB: Remember, in our article, we discussed how to add a CSS file to our HTML document using the <link> element. For those using a local IDE, for you to follow along with this lesson, you have to add the link to your Javascript file to your HTML document using the <link> element contained in our <head> element.
Types of CSS
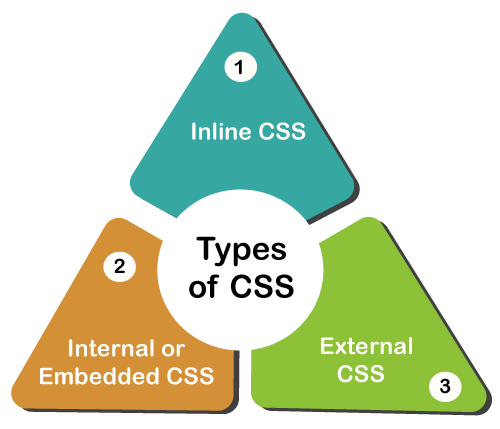
There are three types of CSS, or three methods of including our CSS in the HTML document
Inline CSS
Internal/ Embedded CSS
External CSS
Internal CSS: This features a <style> tag in the HTML document's <head> section. This CSS style is a good approach to styling individual pages.
We can use the internal CSS by embedding it in our HTML <head> element, like so
<head>
<!-- Insert boilerplate code -->
<style type="text/css">
body {
background-color: black;
}
h1 {
color: white;
padding: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
Inside here, we see that our CSS commands are written directly in our HTML. Don't worry about trying to understand the CSS for now. We will get into it shortly.
External CSS: In external CSS, we link the HTML to the external .css file, just as had learned in our Setting up the development environment article. This is a more efficient method for styling a website. By editing the .css file, we can change the whole site at once.
After creating the CSS file, we link it to the HTML document.
.xleftcol {
float: right;
width: 35%;
background:#608800;
}
.xmiddlecol {
float: right;
width: 35%;
background:#eff3df;
}
This is what a standard external CSS document looks like.
Inline CSS:
Inline CSS is used to style a specific HTML element. Add a style attribute to each HTML tag without using the selectors. Managing a website may be difficult if we use only inline CSS. However, inline CSS in HTML is useful in some situations. In the following example, we have used the inline CSS in <p> and <h1> tag.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<!-- Insert boilerplate code -->
<body style="background-color:white;">
<h1 style="color:Red;padding:20px;">CSS Tutorials</h1>
<p style="color:blue;">It will be useful here.</p>
</body>
</html>
CSS Syntax
CSS code, despite where it appears, whether as a stand-alone document or written in the HTML file, has a general syntax.
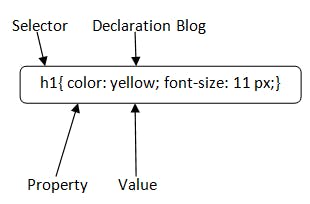
In CSS, we have the selector, the property being worked on, and the style value assigned to that selector. Basically, selectors are representations of our HTML in our CSS code. CSS code is separated by semi-colons ; . In the image above, there are two CSS inputs separated by a semicolon. The color and font-size properties.
CSS code is written with small letters, and compound words are hyphenated. Example: font-size.
CSS selectors
CSS selectors are used to select the HTML element you want to style. Selectors are part of the CSS rule set. CSS selectors select HTML elements according to their id, class, type, attribute, etc.
There are several different types of selectors in CSS.
CSS Element Selector
CSS Id Selector
CSS Class Selector
CSS Universal Selector
CSS Group Selector
Element selector: The element selector selects the HTML element by its name.
Id selector: The id selector selects a specific HTML element with its id attribute. An id is always unique within the page so it is chosen to select a single, unique element. It is written with the hash character (#), followed by the id attribute of the element.
Class Selector: The class selector selects HTML elements with a specific class attribute. It is used with a period character . (full stop symbol) followed by the class name.
There are other forms of selectors, that you can read up on Here.
CSS Box Model
In CSS, the term "box model" is used when talking about design and layout. The CSS box model is essentially a box that wraps around every HTML element. It consists of: margins, borders, padding, and the actual content. The image below illustrates the box model:
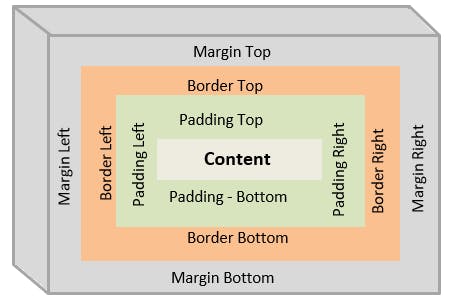
Explanation of the different parts:
Content - The content of the box, where text and images appear
Padding - Clears an area around the content. The
paddingis transparent. The padding property can be modified using the,padding-left,padding-right,padding-top, andpadding-bottomsub-properties.Border - A border that goes around the padding and content. The
borderis transparent. The padding property can be modified using the,border-left,border-right,border-top, andborder-bottomsub-properties.Margin - Clears an area outside the border. The margin is transparent. The
marginis transparent. The padding property can be modified using the,margin-left,margin-right,margin-top, andmargin-bottomsub-properties.
CSS Units
CSS has several different units for expressing a length.
Many CSS properties take "length" values, such as width, margin, padding, font-size, etc. A length is a number followed by a length unit, such as 10px, 2em, etc.
Note: A whitespace cannot appear between the number and the unit. However, if the value is, 0, the unit can be omitted. For some CSS properties, negative lengths are allowed.
Read, and understand more about CSS units here.
Some common CSS properties and their uses
The CSS properties in the example above do not even begin to scratch the surface of all the CSS properties or sub-properties available for use.
As a developer, it is important that we learn to leverage the power of Google (or our search engine of choice) to help us with concepts that are difficult to understand or even remember. As with HTML, there are so many CSS properties, and you are not required to remember all of them at once. This is why you should make various documentations your best friends. For web development, there are some pretty good documentations that you can check out: W3schools, which we have referenced a lot. MDN web docs also.
Yaaay!! Congratulations, you just finished your first class in CSS!
I am so excited! I had so much fun writing this. I hope you have as much fun reading, and practicing this, as I did writing it.
See you all next week in our advanced CSS class!
